BIDIRECTIONAL STATIC LOAD TEST
Regarded as one of the safest and most efficient techniques for capturing data relating to soil and foundation response under load, a bi-directional static load test (BDSLT) involves internally placing a load-cell at one or more specific locations along its length.
The jack applies force simultaneously upward against the shaft resistance above its location and downward against the combined resistance below the jack assembly (including the toe or base resistance).
The cage is equipped with instrumentation to measure shaft and toe movements, as well as soil resistance from the applied load. Load-cells can be installed in various types of deep foundation elements, including bore holes and continuous flight auger (CFA).
Bi-Directional Static Load Test Benefits include
- High-capacity static load test method for deep foundation elements.
- Separates soil/rock resistance and movement data for shaft and toe.
- Determines magnitude of the mobilised shaft and toe resistances.
- Embedded strain gauges within the foundation element determine the soil/rock resistance distribution along the foundation length for optimizing foundation design.
- Not restricted by structural or geotechnical limit of load frame, reaction beams, or reaction piles.
- Multiple Load-Cells can be used at a single jack assembly location or at multiple jack assembly locations to apply larger loads.


Bi-directional Static Load Test cage being lifted for Armadale Line Upgrade Alliance, East Victoria Park
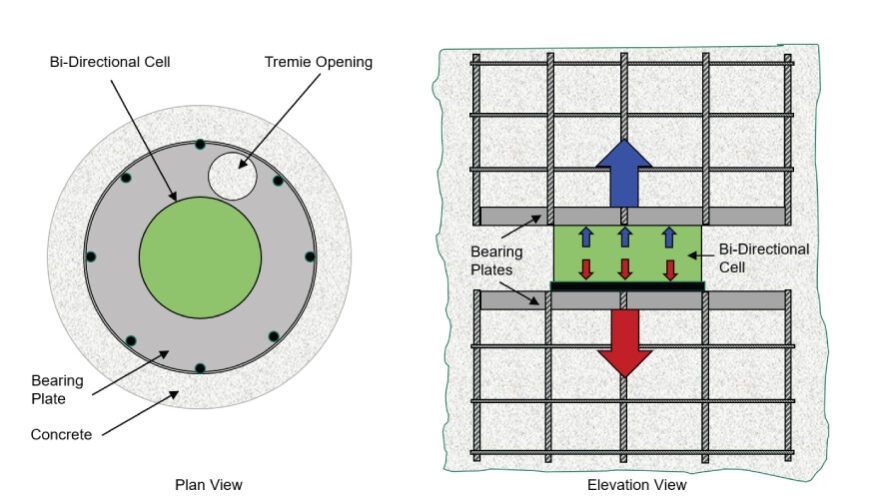
Generalized plan and elevation views of single Load-Cell jack assemblies

Generalized plan and elevation views of multiple Load-Cell jack assemblies
Bi-Directional Static Load Testing (BDSLT) is standardized by ASTM D8169 – Standard Test Methods for deep foundations under Bi-Directional Static Axial Compressive Load.
In drilled shafts, the configuration of the jack assembly to accommodate the cells as well as tremie pipe or pump line location is important for concrete placement.
